Back to all products
Product criteria
| Neuronal TGase (TG6) ELISA |
| Celiac disease antigens |
| Deamidated gliadin peptides |
| Further products for CD research |
| Non-CD antigens |
Product criteria
| Source |
|---|
| E. coli 8 |
| Diagnostics |
| Celiac Disease antigen 4 |
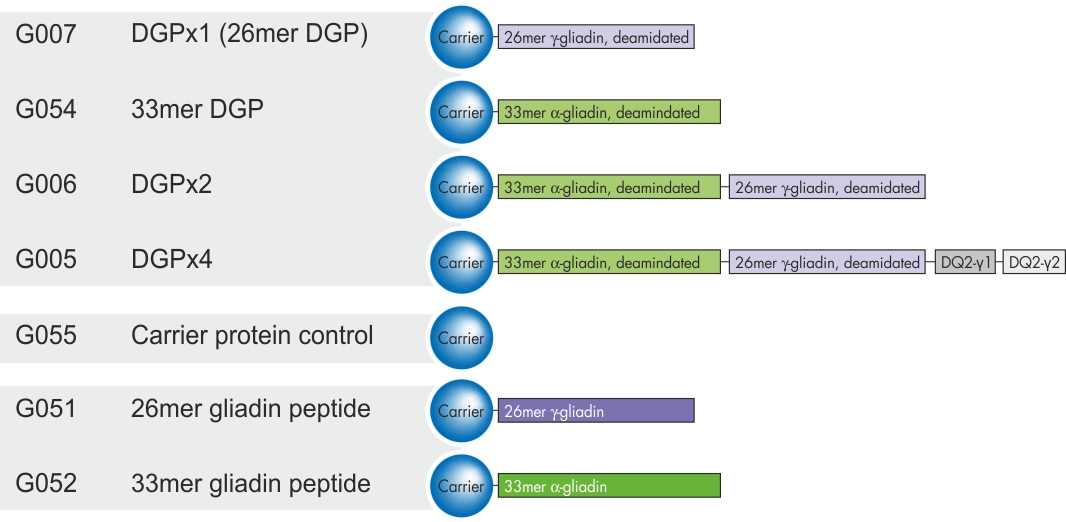
Deamidated gliadin peptides
Detection of gliadin antibodies has been used for a long time in celiac disease diagnostics but suffered from low specificity. This disadvantage was overcome by the introduction of deamidated gliadin peptides as the antigen.
The rationale behind this change is that tissue transglutaminase catalyzes gliadin deamidation in the intestinal mucosa of celiac disease patients, resulting in deamidated gliadin peptides which are recognized by HLA receptors of immune cells. Therefore, deamidated gliadin antibodies are specific for celiac disease.
We introduced four different variations of deamidated gliadin antigens composed of a carrier protein linked with a combination of the deamidated 33-mer and 26-mer gamma gliadin peptides and the DQ2-GI- and DQ2-GII-peptides (Dørum S. et al., J Proteome Res. 2009; 8:1748-55).
In addition, the non-deamidated native versions as well as the control carrier protein are available (Section: Cereal Proteins).
The rationale behind this change is that tissue transglutaminase catalyzes gliadin deamidation in the intestinal mucosa of celiac disease patients, resulting in deamidated gliadin peptides which are recognized by HLA receptors of immune cells. Therefore, deamidated gliadin antibodies are specific for celiac disease.
We introduced four different variations of deamidated gliadin antigens composed of a carrier protein linked with a combination of the deamidated 33-mer and 26-mer gamma gliadin peptides and the DQ2-GI- and DQ2-GII-peptides (Dørum S. et al., J Proteome Res. 2009; 8:1748-55).
In addition, the non-deamidated native versions as well as the control carrier protein are available (Section: Cereal Proteins).

 Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification
Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification  Besuch des Bundesministers für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz Dr. Robert Habeck bei der Zedira
Besuch des Bundesministers für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz Dr. Robert Habeck bei der Zedira  Discover Our New Catalogue Edition and Dive into the World of Transglutaminases!
Discover Our New Catalogue Edition and Dive into the World of Transglutaminases!  Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification
Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification  Dr. Falk Pharma and Zedira announce successful completion of the phase 2a proof-of-concept study of ZED1227 for the treatment of Celiac Disease
Dr. Falk Pharma and Zedira announce successful completion of the phase 2a proof-of-concept study of ZED1227 for the treatment of Celiac Disease  Dr. Falk Pharma und Zedira verkünden den erfolgreichen Abschluss der Phase 2a-Studie mit ZED1227 zur Behandlung von Zöliakie
Dr. Falk Pharma und Zedira verkünden den erfolgreichen Abschluss der Phase 2a-Studie mit ZED1227 zur Behandlung von Zöliakie  Reversibly acting transglutaminase 2 inhibitors: drug candidates for the treatment of fibrosis
Reversibly acting transglutaminase 2 inhibitors: drug candidates for the treatment of fibrosis  Transcriptomic analysis of the efficacy of TG2-inhibitor trials and human intestinal organoids modelling Celiac disease pathogenesis
Transcriptomic analysis of the efficacy of TG2-inhibitor trials and human intestinal organoids modelling Celiac disease pathogenesis  Transglutaminase antibodies and neurological manifestations of gluten sensitivity
Transglutaminase antibodies and neurological manifestations of gluten sensitivity  Design of Oral FXIIIa Blockers as Safer Anticoagulants Mission Impossible?
Design of Oral FXIIIa Blockers as Safer Anticoagulants Mission Impossible?  Microbial transglutaminase (MTG) enables efficient and site-specific conjugation to native antibodies without the need of antibody engineering
Microbial transglutaminase (MTG) enables efficient and site-specific conjugation to native antibodies without the need of antibody engineering  Tridegin as FXIIIa inhibitor
Tridegin as FXIIIa inhibitor  Microbial transglutaminase: from discovery to market
Microbial transglutaminase: from discovery to market  Tissue transglutaminase inhibitors
Tissue transglutaminase inhibitors  Tissue transglutaminase in Alzheimers Disease
Tissue transglutaminase in Alzheimers Disease  Factor XIIIa: novel target for anticoagulation?
Factor XIIIa: novel target for anticoagulation?  Microbial transglutaminase for site-specific protein conjugation
Microbial transglutaminase for site-specific protein conjugation