News
Link  Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification
Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification
 Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification
Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification Link Zedira supports the Tampere Celiac Disease Symposium 2025
Link Co-authored article published in Nature Immunology: Transcriptomic analysis of intestine following administration of a transglutaminase 2 inhibitor to prevent gluten-induced intestinal damage in celiac disease
Link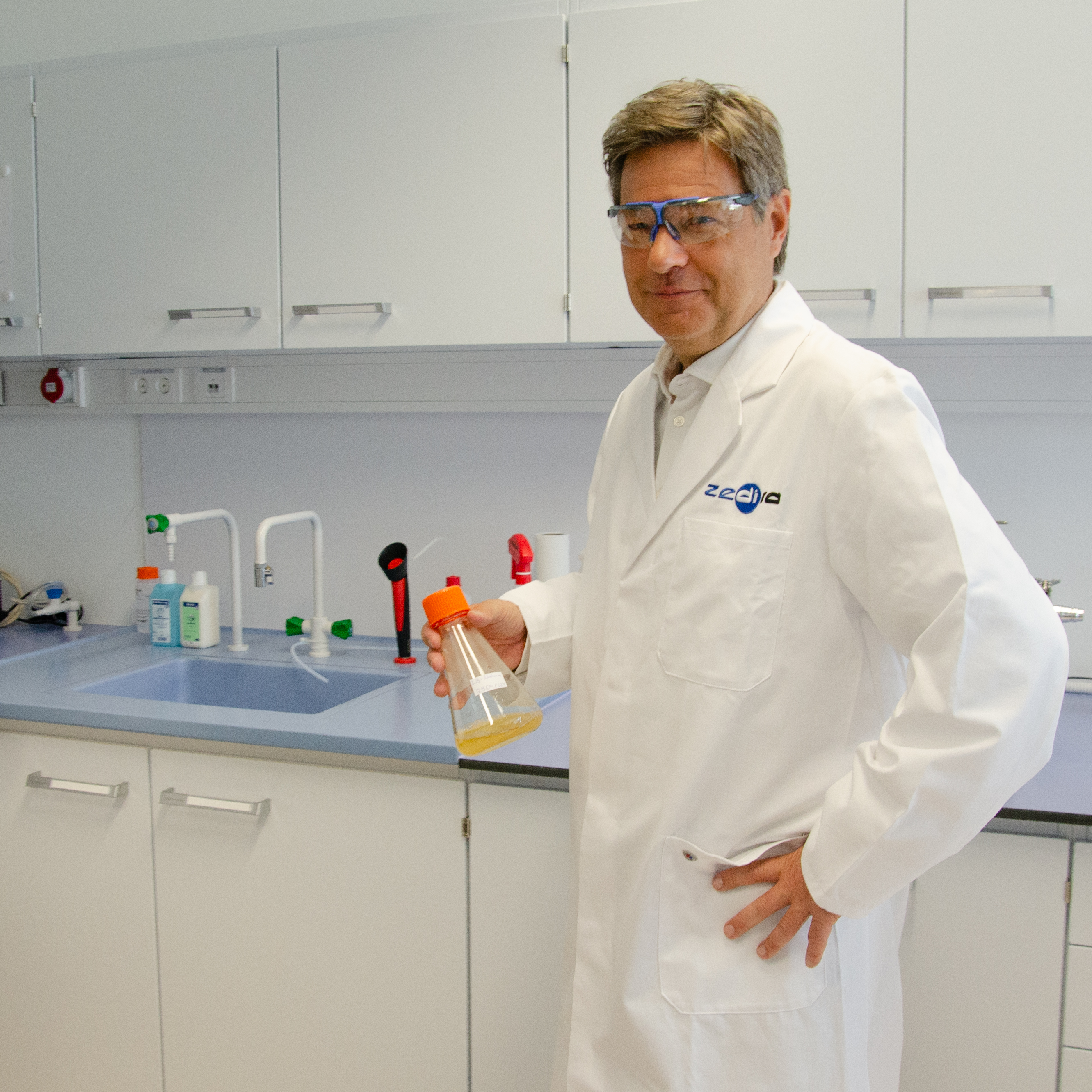  Besuch des Bundesministers für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz Dr. Robert Habeck bei der Zedira
Besuch des Bundesministers für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz Dr. Robert Habeck bei der Zedira
 Besuch des Bundesministers für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz Dr. Robert Habeck bei der Zedira
Besuch des Bundesministers für Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz Dr. Robert Habeck bei der Zedira Link  Discover Our New Catalogue Edition and Dive into the World of Transglutaminases!
Discover Our New Catalogue Edition and Dive into the World of Transglutaminases!
 Discover Our New Catalogue Edition and Dive into the World of Transglutaminases!
Discover Our New Catalogue Edition and Dive into the World of Transglutaminases! Link Co-authored article: The Oral Transglutaminase 2 Inhibitor ZED1227 Accumulates in the Villous Enterocytes in Celiac Disease Patients during Gluten Challenge and Drug Treatment
Link Takeda Enters Collaboration and Licensing Agreement with Zedira and Dr. Falk Pharma to Develop First-in-Class Celiac Disease Therapy
Link Kooperations- und Lizenzvereinbarung zwischen Takeda, Zedira und Dr. Falk Pharma zur Entwicklung einer First-in-Class-Therapie für die Zöliakie
Link Co-authored posters at ICDS 2022
Link  Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification
Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification
 Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification
Successful ISO9001:2015 recertification Link Dr. Falk Pharma and Zedira announce start of the phase 2a proof of concept study of ZED1227 for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Link Zedira publication - Features of ZED1227: The First-In-Class Tissue Transglutaminase Inhibitor Undergoing Clinical Evaluation for the Treatment of Celiac Disease
Link Dr. Falk Pharma and Zedira announce start of the phase 2b real-life study of ZED1227 for the treatment of Celiac Disease
Link  Dr. Falk Pharma and Zedira announce successful completion of the phase 2a proof-of-concept study of ZED1227 for the treatment of Celiac Disease
Dr. Falk Pharma and Zedira announce successful completion of the phase 2a proof-of-concept study of ZED1227 for the treatment of Celiac Disease
 Dr. Falk Pharma and Zedira announce successful completion of the phase 2a proof-of-concept study of ZED1227 for the treatment of Celiac Disease
Dr. Falk Pharma and Zedira announce successful completion of the phase 2a proof-of-concept study of ZED1227 for the treatment of Celiac Disease Link  Dr. Falk Pharma und Zedira verkünden den erfolgreichen Abschluss der Phase 2a-Studie mit ZED1227 zur Behandlung von Zöliakie
Dr. Falk Pharma und Zedira verkünden den erfolgreichen Abschluss der Phase 2a-Studie mit ZED1227 zur Behandlung von Zöliakie
 Dr. Falk Pharma und Zedira verkünden den erfolgreichen Abschluss der Phase 2a-Studie mit ZED1227 zur Behandlung von Zöliakie
Dr. Falk Pharma und Zedira verkünden den erfolgreichen Abschluss der Phase 2a-Studie mit ZED1227 zur Behandlung von Zöliakie Link  Reversibly acting transglutaminase 2 inhibitors: drug candidates for the treatment of fibrosis
Reversibly acting transglutaminase 2 inhibitors: drug candidates for the treatment of fibrosis
 Reversibly acting transglutaminase 2 inhibitors: drug candidates for the treatment of fibrosis
Reversibly acting transglutaminase 2 inhibitors: drug candidates for the treatment of fibrosis Blog
Link  Transcriptomic analysis of the efficacy of TG2-inhibitor trials and human intestinal organoids modelling Celiac disease pathogenesis
Transcriptomic analysis of the efficacy of TG2-inhibitor trials and human intestinal organoids modelling Celiac disease pathogenesis
 Transcriptomic analysis of the efficacy of TG2-inhibitor trials and human intestinal organoids modelling Celiac disease pathogenesis
Transcriptomic analysis of the efficacy of TG2-inhibitor trials and human intestinal organoids modelling Celiac disease pathogenesis Link  Transglutaminase antibodies and neurological manifestations of gluten sensitivity
Transglutaminase antibodies and neurological manifestations of gluten sensitivity
 Transglutaminase antibodies and neurological manifestations of gluten sensitivity
Transglutaminase antibodies and neurological manifestations of gluten sensitivity Link DZG Aktuell: Aufruf zur Teilnahme an einer weiteren Wirksamkeitsstudie mit dem Studienmedikament ZED1227
Link  Design of Oral FXIIIa Blockers as Safer Anticoagulants Mission Impossible?
Design of Oral FXIIIa Blockers as Safer Anticoagulants Mission Impossible?
 Design of Oral FXIIIa Blockers as Safer Anticoagulants Mission Impossible?
Design of Oral FXIIIa Blockers as Safer Anticoagulants Mission Impossible? Link 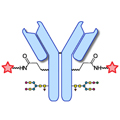 Microbial transglutaminase (MTG) enables efficient and site-specific conjugation to native antibodies without the need of antibody engineering
Microbial transglutaminase (MTG) enables efficient and site-specific conjugation to native antibodies without the need of antibody engineering
 Microbial transglutaminase (MTG) enables efficient and site-specific conjugation to native antibodies without the need of antibody engineering
Microbial transglutaminase (MTG) enables efficient and site-specific conjugation to native antibodies without the need of antibody engineering Link 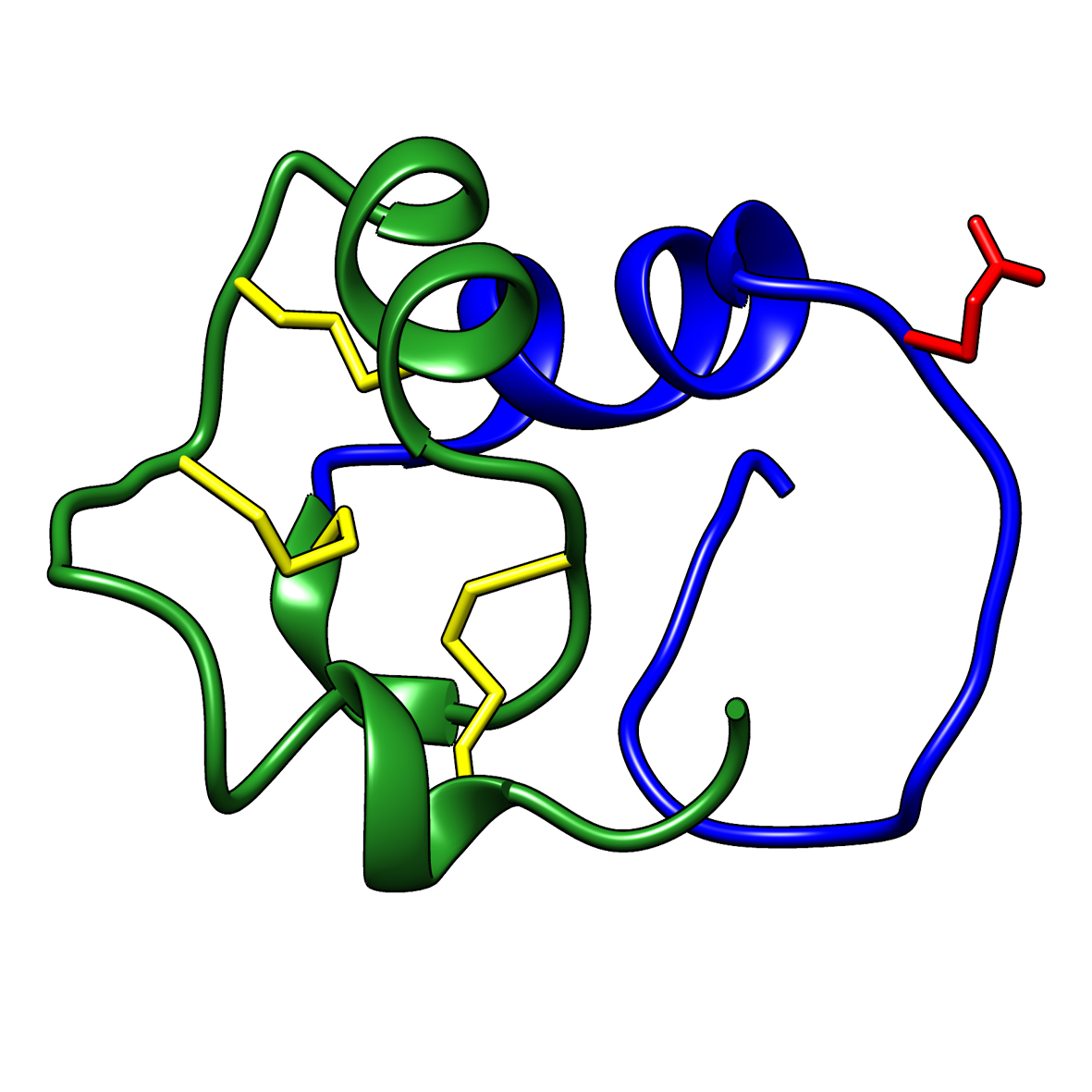 Tridegin as FXIIIa inhibitor
Tridegin as FXIIIa inhibitor
 Tridegin as FXIIIa inhibitor
Tridegin as FXIIIa inhibitor Link 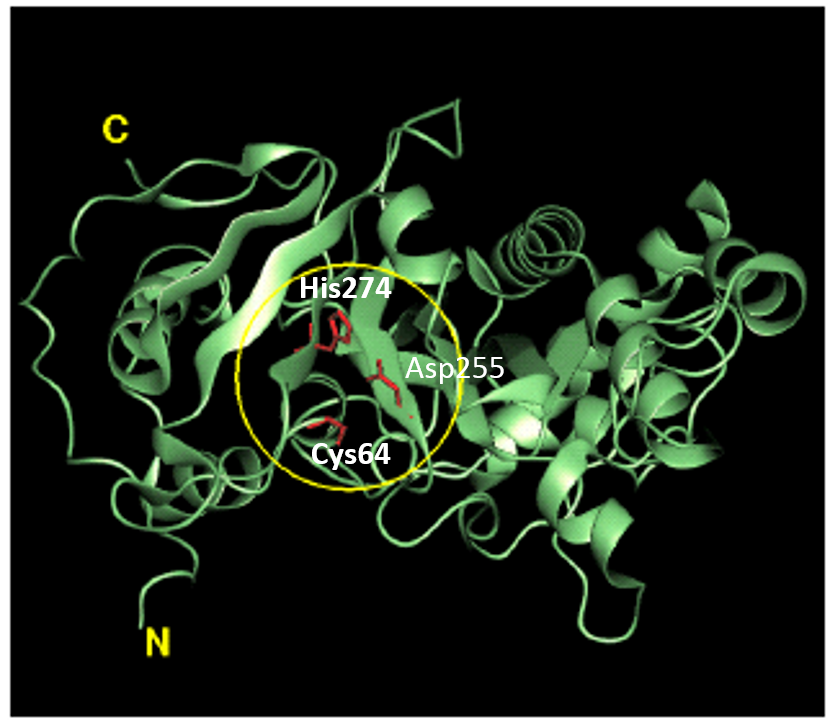 Microbial transglutaminase: from discovery to market
Microbial transglutaminase: from discovery to market
 Microbial transglutaminase: from discovery to market
Microbial transglutaminase: from discovery to market Link  Tissue transglutaminase inhibitors
Tissue transglutaminase inhibitors
 Tissue transglutaminase inhibitors
Tissue transglutaminase inhibitors Link  Tissue transglutaminase in Alzheimers Disease
Tissue transglutaminase in Alzheimers Disease
 Tissue transglutaminase in Alzheimers Disease
Tissue transglutaminase in Alzheimers Disease Link  Factor XIIIa: novel target for anticoagulation?
Factor XIIIa: novel target for anticoagulation?
 Factor XIIIa: novel target for anticoagulation?
Factor XIIIa: novel target for anticoagulation? Link  Microbial transglutaminase for site-specific protein conjugation
Microbial transglutaminase for site-specific protein conjugation
 Microbial transglutaminase for site-specific protein conjugation
Microbial transglutaminase for site-specific protein conjugation Link Transglutaminases: current research and applications - future directions
Events
World ADC 2025
Date: 03.11.2025 - 06.11.2025
Location: San Diego, USA
Date: 03.11.2025 - 06.11.2025
Location: San Diego, USA
Society for Biomaterials 2026 Annual Meeting & Exposition
Date: 25.03.2026 - 28.03.2026
Location: Atlanta, USA
Date: 25.03.2026 - 28.03.2026
Location: Atlanta, USA
TERMIS EU-Chapter 2026
Date: 21.04.2026 - 24.04.2026
Location: Palma de Mallorca, Spain
Date: 21.04.2026 - 24.04.2026
Location: Palma de Mallorca, Spain
Conference on Transglutaminases in Biological Processes
Date: 25.05.2026 - 29.05.2026
Location: Padua, Italy
Date: 25.05.2026 - 29.05.2026
Location: Padua, Italy
Annual Conference of the European Society for Biomaterials
Date: 07.09.2026 - 11.09.2026
Location: Antwerp, Belgium
Date: 07.09.2026 - 11.09.2026
Location: Antwerp, Belgium
21st International Celiac Disease Symposium 2026
Date: 17.11.2026 - 20.11.2026
Location: Melbourne, Australia
Date: 17.11.2026 - 20.11.2026
Location: Melbourne, Australia